What Is Oral Sedation?
Oral sedation is the unacknowledged hero in dentistry that changed how people feel during those unpleasant dental procedures. If the notion of being in the dentist’s chair makes you nervous or brings up unpleasant experiences, you are not alone. Millions of individuals worldwide are afflicted with dental anxiety, which makes them put off or forgo necessary oral care, which can negatively affect their general health.
Dental anxiety does have a silver lining, though, and it comes in the shape of oral sedation. This amazing approach has transformed dental treatment by providing patients with a safe, pleasant, and anxiety-free alternative.
Learn everything about oral sedation that helps you eliminate your fear of the dentist and welcome a healthier smile.
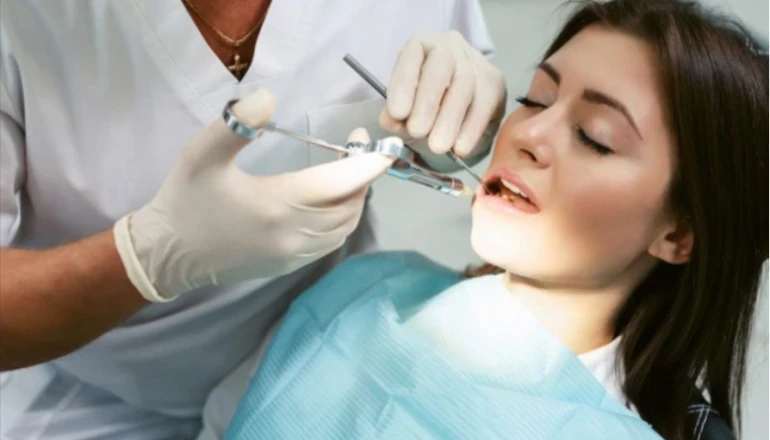
Oral sedation is a dentistry method used to reduce anxiety and help patients unwind when a dentist performs dental procedures. It entails the delivery of oral drugs, usually taken orally before the dental session, in tablets or liquid. These drugs are part of a group of medicines known as benzodiazepines, which include sedative, anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing), and muscle-relaxing characteristics.
Due to its practicality and success in easing dental anxiety, oral sedation is frequently recommended by both patients and dentists. Depending on the patient’s demands and how complicated the dental operation is, a different drug and dose may be utilized for oral sedation. To select the most effective sedation method, dentists carefully consider the patient’s medical history, level of anxiety, and anticipated session length.
What Are The Types Of Oral Sedation?
1. Nitrous Oxide
2. Oral Conscious Sedation
3. Intravenous (IV) Sedation
How Strong Is An Oral Sedative?
- Mild dental procedures can be performed safely and effectively while under the influence of mild sedatives.
- Moderate sedation, frequently used for more involved operations, offers a deeper sensation of relaxation and may cause sleepiness.
- Deep sedation, which may be attained with greater dosages, is usually saved for lengthy or invasive procedures.